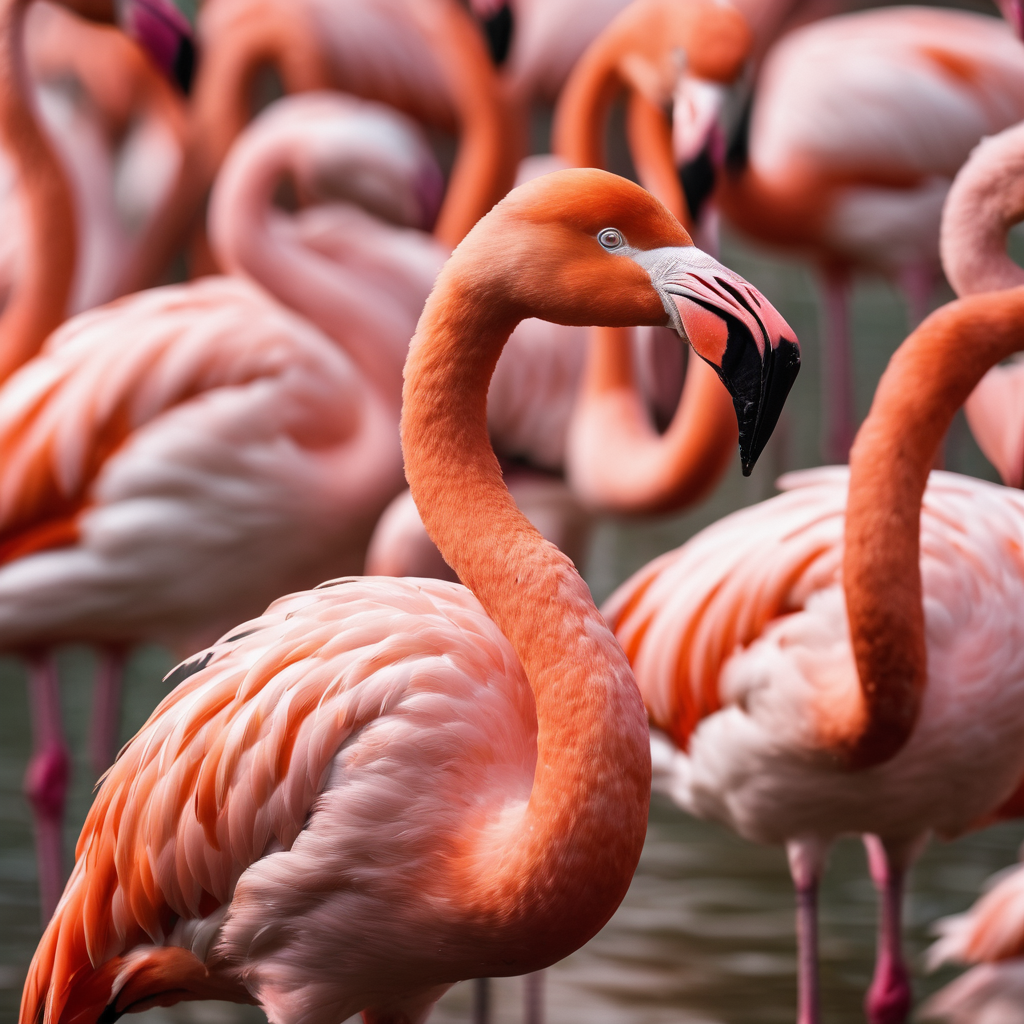
The Smooth Flamingo: Nature’s Living Workmanship
Flamingos are among the most famous and outwardly striking birds on the planet, known for their dynamic pink plumes, long legs, and exquisite necks. These birds dazzle the creative mind with their special ways of behaving and natural surroundings, making them a subject of interest for bird watchers and researchers the same. This article investigates the universe of flamingos, digging into their environments, diets, ways of behaving, and the preservation challenges they face.

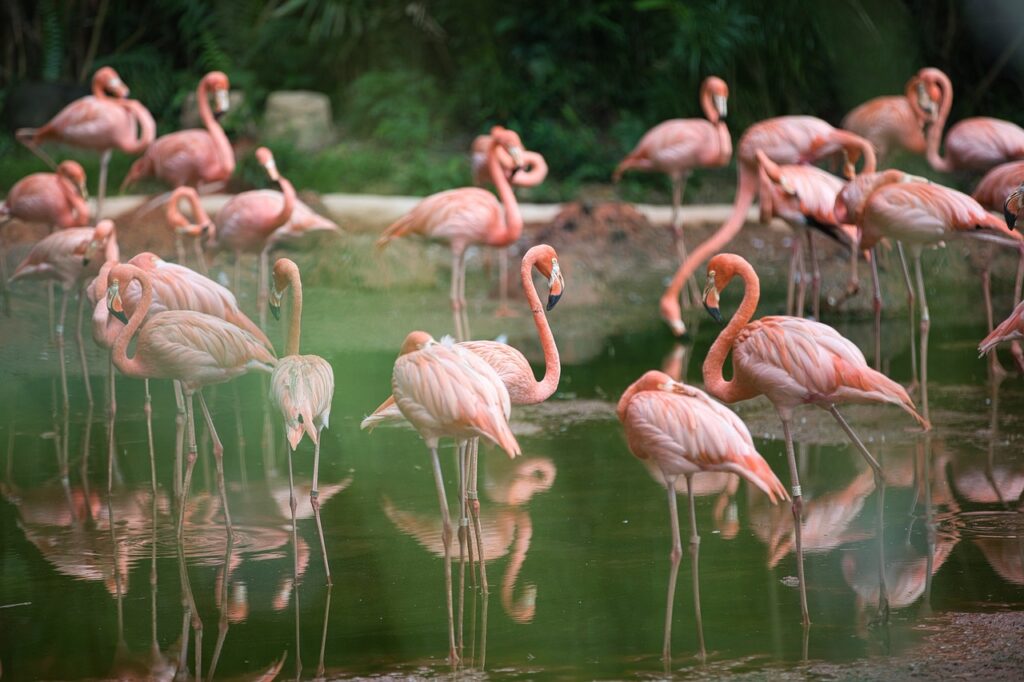
Natural surroundings and Appropriation
care tracked down in different areas of the planet, occupying locales in Africa, Asia, the Americas, and Europe. They commonly live in enormous, shallow lakes, tidal ponds, mangrove marshes, and sandy islands where the water is pungent or salty. These living spaces give the fundamental food assets and favorable places that flamingos need to flourish. The absolute most notable flamingo living spaces incorporate the soluble pools of East Africa, the salt pads of the Andes, and the beach front districts of the Caribbean and South America.

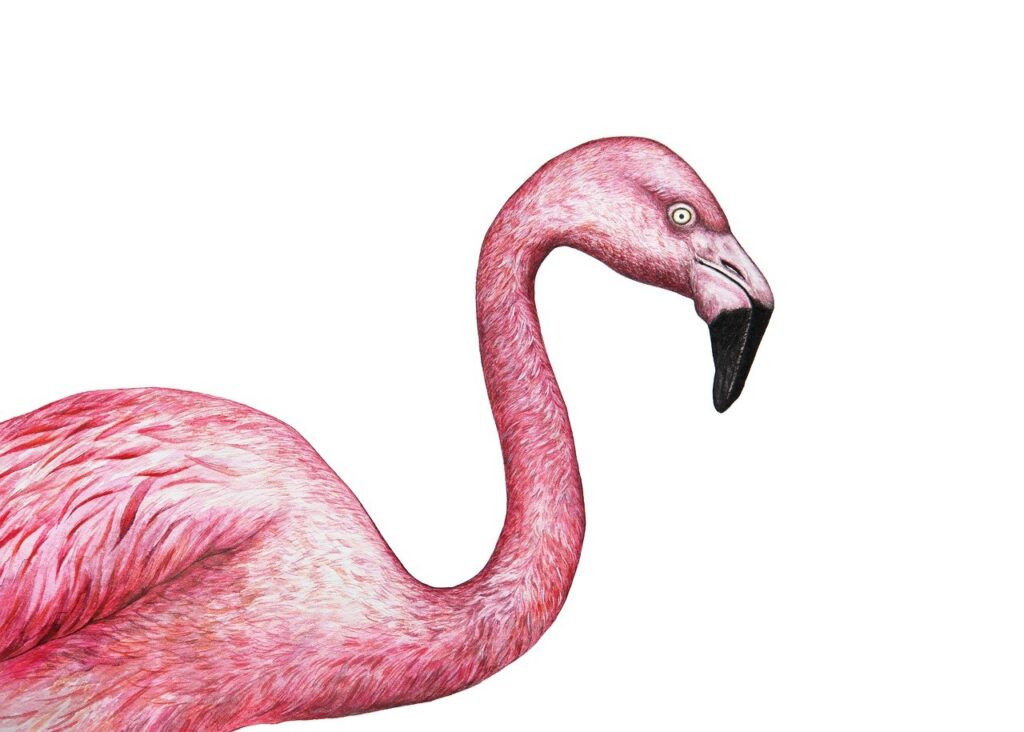
Actual Qualities Flamingos
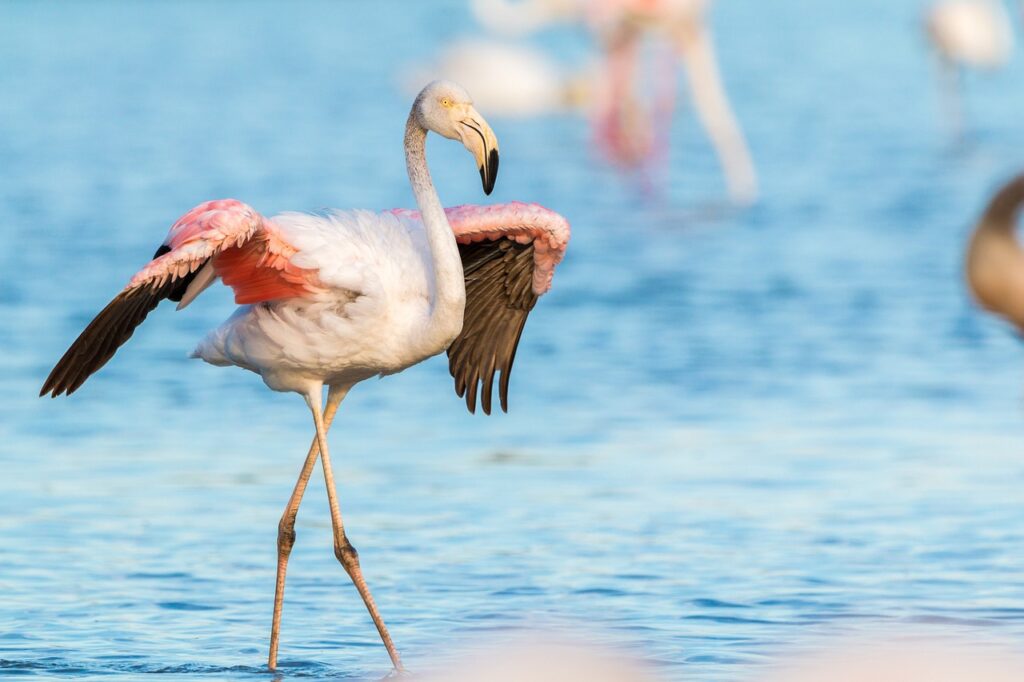
Flamingos are effectively conspicuous because of their unmistakable pink or ruddy pink plumage, which is a consequence of the carotenoid colors tracked down in their eating regimen. These colors are gotten from the green growth, diatoms, and little scavengers that flamingos consume. Their long, thin legs and webbed feet are flawlessly adjusted for swimming in shallow waters, while their particular mouths permit them to channel feed on little organic entities in the water. Flamingos likewise have a one of a kind construction in their mouths that empowers them to take care of by holding their heads topsy turvy.
Conduct and Social Design
Flamingos are exceptionally friendly birds, frequently found in enormous herds that can number in the large numbers. This social design gives various benefits, including upgraded assurance from hunters and more proficient scavenging. Inside these herds, flamingos take part in different synchronized ways of behaving, for example, dressing, taking care of, and the notorious gathering “walking” shows during mating ceremonies. These presentations include facilitated developments and vocalizations, assisting with reinforcing social bonds and draw in mates.
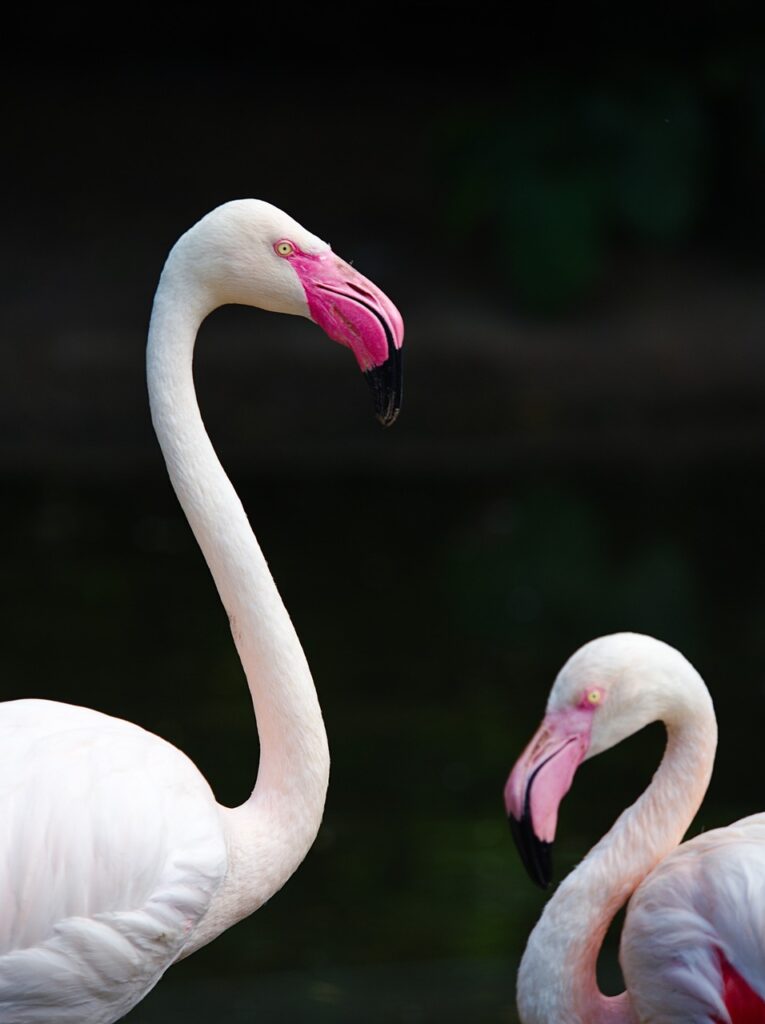

Diet and Taking care of Propensities
Flamingos are channel feeders, utilizing their specific bills to filter through mud and water to catch their food. They feed fundamentally on green growth, diatoms, little shellfish, and other minuscule life forms. Their snouts have lamellae, which are brush like designs that assist with catching food particles. Flamingos frequently work up the mud with their feet to carry food to the surface and afterward utilize their noses to sift it through.

Propagation and Life expectancy
Flamingos ordinarily breed in enormous settlements, where they fabricate home hills out of mud to keep their eggs above water. The female generally lays a solitary egg, which the two guardians alternate brooding. After around 27-31 days, the egg hatches, and the chick is taken care of a nutritious “crop milk” created by the two guardians. Flamingo chicks are brought into the world with dim or white down feathers and don’t gain their pink hue until they are around 2-3 years of age. Flamingos can live for 20 to 30 years in the wild, for certain people in imprisonment living considerably longer.
Preservation Difficulties
In spite of their wide circulation, flamingos face a few dangers that risk their populaces. Living space misfortune because of human exercises like mining, farming, and metropolitan improvement is a huge concern. Contamination, environmental change, and unsettling influences from the travel industry additionally present difficulties to their endurance. Preservation endeavors are in progress to safeguard basic flamingo territories and bring issues to light about the significance of protecting these one of a kind environments.
End
Flamingos are an image of effortlessness and magnificence in the normal world, dazzling individuals with their staggering appearance and captivating ways of behaving. Understanding their nature and the difficulties they face is pivotal for guaranteeing their preservation and the wellbeing of the biological systems they occupy. By safeguarding flamingos and their natural surroundings, we assist with saving the biodiversity and excellence of our planet for people in the future to appreciate and appreciate.
A significant part of the time Presented Requests about Flamingos
1. Why are flamingos pink?
Flamingos get their pink or reddish pink tone from the carotenoid colors in their eating schedule, which consolidates green development, diatoms, and little shellfish. These varieties are isolated in the liver and saved in the skin and crest, giving flamingos their specific color.
2. Where do flamingos live?
Flamingos are found in different districts all around the planet, including segments of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and Europe. They consistently have tremendous, shallow lakes, lagoons, mangrove bogs, and sandy islands with saline or unforgiving water.
3. What do flamingos eat?
Flamingos are channel feeders, consuming green development, diatoms, little scavangers, and other moment natural elements. They use their particular bills, which contain brush like plans called lamellae, to channel food from the water and mud.
4. How do flamingos breed and raise their young?
Flamingos breed in colossal settlements and manufacture home slopes out of mud to keep their eggs above water. The female lays a lone egg, which the two watchmen substitute agonizing for around 27-31 days. Following deliver, the chick is dealt with a nutritious “crop milk” made by the two watchmen. Flamingo chicks are carried into the world with dull or white down plumes and cultivate their pink concealing more than 2-3 years.
5. What are the important threats to flamingos?
Flamingos face a couple of risks, including normal environmental factors hardship in view of mining, cultivating, and metropolitan new development. Tainting, natural change, and aggravations from the movement business in like manner present basic troubles. Conservation tries revolve around shielding fundamental conditions and exposing issues about the meaning of safeguarding these clever natural frameworks.

